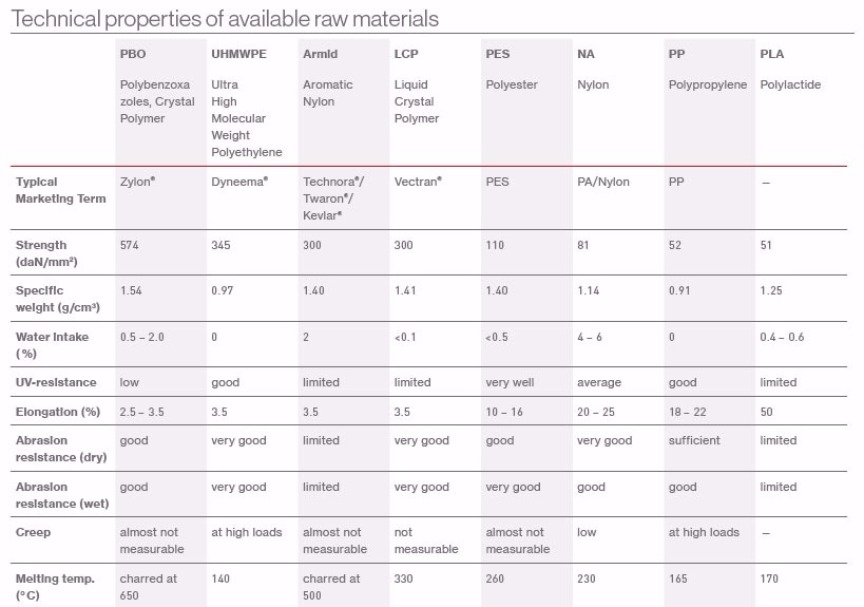
Raw Material
The safety and rescue ropes of TEUFELBERGER consist of different raw materials that influence the performance of the rope and its characteristics.
PBO (Polybenzoxazoles, Crystal Polymer)
The generic fiber PBO refers to Zylon® which is a high performance fiber with the highest strength and lowest stretch of any commercially available fiber. It is extremely expensive and experiences progressive strength loss when exposed to UV-rays.
UHMWPE (Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene)
UHMWPE (also known as UHMPE or HMPE Dyneema®) is an extremely high strength fiber of ultra high molecular polyethylene. For the same weight it has 15 times the tensile strength of steel. Rope made from this type of fiber shows very low elongation and tensile strength. If very high loads are being applied for a long period of time, UHMWPE fiber tends to creep. The rope then is irreversibly extending its length. At the same time, these robust fibers show excellent performance in terms of abrasion resistance and good UV-resistance.
Aramid (Aromatic Nylon)
Aramid fibers have an extremely high breaking load and show almost no stretch. On the other hand they are sensitive to UV-rays, bending over sharp edges, and abrasion. It is mainly used in places where high temperature resistance is essential, for example on winches, in hot air balloon ropes, or for any other application where heat exposure needs to be considered.
LCP (Liquid Crystal Polymer)
LCP (known as Vectran®, a brand name of Hoechst Celanese), combines extremely low elongation with extremely high breaking loads. However, ist UV-resistance is not very high. It is heat resistant and not very sensitive to bending over sharp edges. The big advantage of Vectran® is, however, that compared to UHMWPE it does not creep.
PES (Polyester)
Static ropes made of polyester fibers are characterized by good breaking loads and low stretch. This material offers both chemical and physical advantages such as UV resistance salt water resistance, and good abrasion strength in both dry and wet conditions. However, the dynamic energy absorption capacity is much lower than that of nylon ropes and therefore only to a limited extent suitable for types of use involving high impact forces.
NY (Nylon)
Nylon has a high breaking load as well as high elongation. Preferably, it is used in products that are required to absorb shock loads. The abrasion resistance of nylon is better in wet conditions than in dry conditions because it tends to take up water (up to 7%). Kept in wet conditions for too long, the material can become stiff. Another disadvantage compared to polyester is the lower resistance to UV-radiation in sunlight.
PP (Polypropylene)
Due to its limited technical characteristics, polypropylene is only used for simple applications. PP is very light and even buoyant in water. Its abrasion resistance and temperature resistance are lower than those of most other fibers.
PLA (Polylactide)
In technical aspects, PLA yarn is not different from regular synthetic fibers: PLA fiber products also look and feel the same. Polylactic acid is derived from natural sugar resources – which are in turn photosynthesized from CO2 in plants. They are biodegradable under a specific industrial process. The material can be regarded as “CO2-neutral” and is therefore renewable.